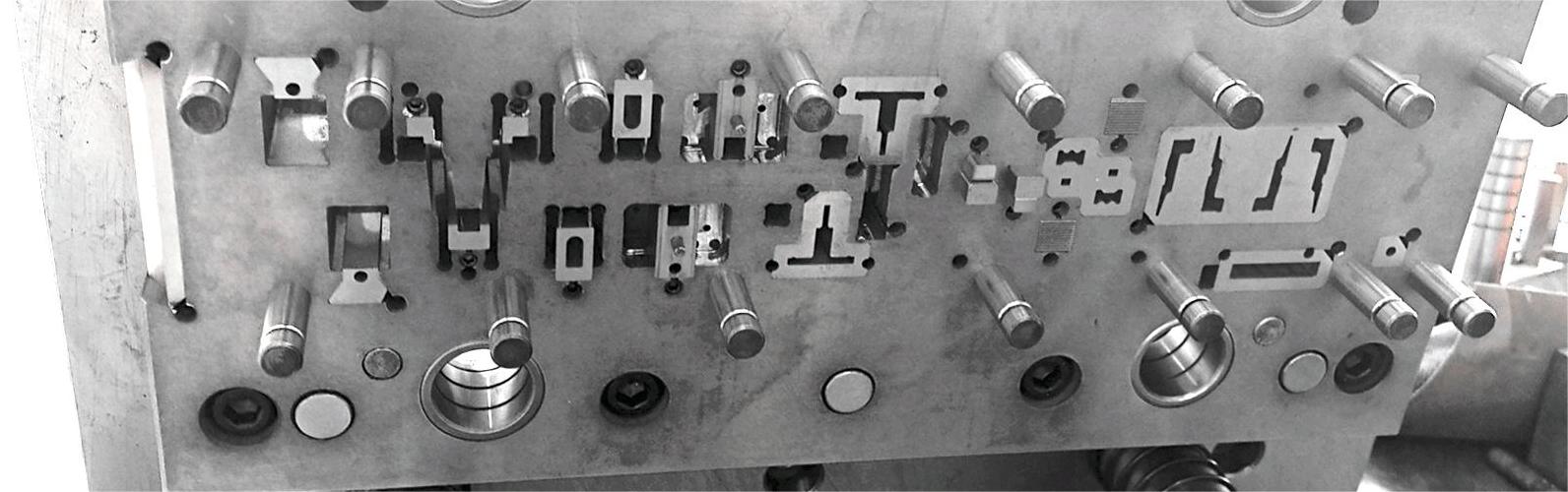

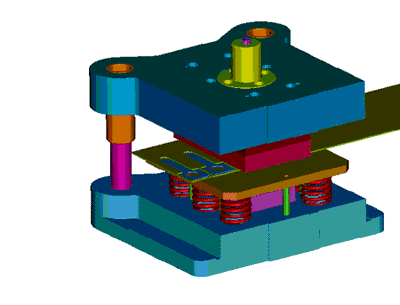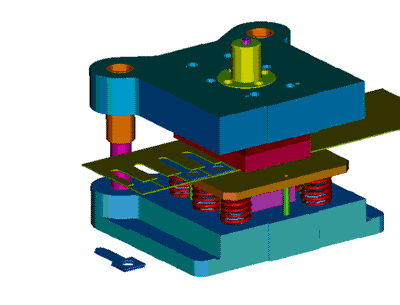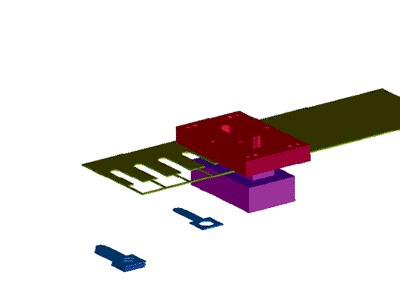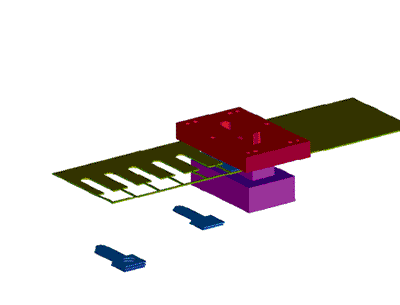






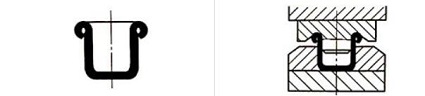

When designing positioning parts, you should consider the convenience of operation, there should be no positioning, and the position should be easy to observe. It is best to use forward positioning, outer profile positioning, and guiding pin positioning.
Pressing, unloading, and discharging components:
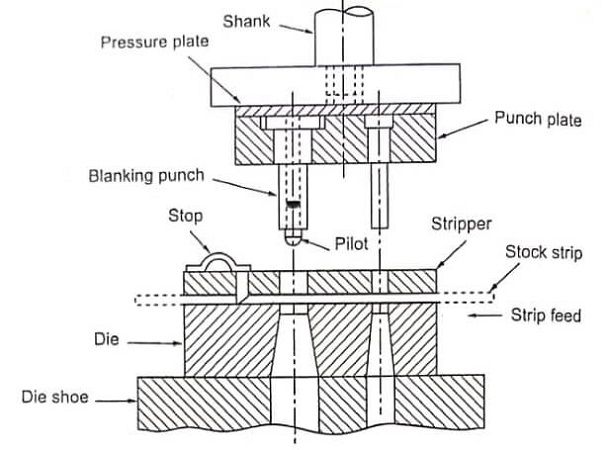
The blanking parts include a blanking ring, blanking board, etc. The blank holder can exert pressure on the drawn blank, thereby preventing the blank from arching and forming wrinkles under the action of tangential pressure.
The function of the holding plate is to prevent the blank from moving and bouncing.
The function of the ejector and unloading plate is to facilitate the ejection of parts and the cleaning of waste. They are supported by springs, rubbers, and air cushion pushrods on the equipment, and can move up and down.
The ejector pins should have sufficient ejection force and the movement should be limited. The unloading board should minimize the closed area or mill an empty slot in the operating position.
The exposed unloading plate shall be surrounded by protective plates to prevent people from reaching out with fingers or foreign objects from entering, and the edges and corners of the exposed surface shall be blunt.
Guide components:
Guide bushings and guide pins are the most widely used guide components. Its function is to ensure that the convex and concave dies have a precise fit clearance during the stamping work.
Therefore, the gap between the guide bushing and the guide pin should be smaller than the blanking gap. The guide bushing is set on the lower mold base, and the upper-end surface of the guide pin is at least 5 to 10 mm above the top surface of the upper template at the bottom dead center of the stroke.
The guide bushing should be arranged far away from the module and the pressing plate so that the operator’s arm does not need to cross the guide bushing to feed and take materials.
Support pillar and mold clamp
It includes upper and lower templates, mold handles, fixed plates for convex and concave molds, backing plates, stoppers, mold clamp, etc. The upper and lower templates are the basic components of the die; various other components are installed and fixed on it.
The plane size of the template, especially the front and rear direction, should be compatible with the workpiece, too large or too small is not conducive to operation.
Some molds (blanking, punching molds) need to set up a backing plate under the mold base for the convenience of parting. At this time, it is better to connect the backing plate and the template with screws, and the thickness of the two backing plates should be absolutely equal.
The spacing of the backing plates shall be subject to the parts that can be delivered and should not be too large to prevent the template from breaking.
Fasteners:
It includes screws, nuts, springs, pins, washers, etc.Standard parts are generally used. There are a lot of standard components of stamping dies, and the design and selection should ensure the needs of tightening and elastic ejection, avoiding the fasteners from being exposed on the surface operation position, and preventing hand injury and hindering operation.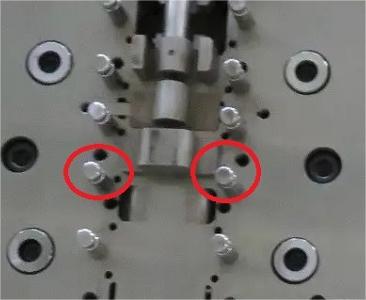
Provide Comprehensive Product Technology Solutions


Need more Stamping mold and molding information? Please contact with us